Exec
The Exec resource lets you execute scripts and commands either locally on the host machine or remotely inside containers. It provides a flexible way to automate environment setup, system configuration, and custom workflows as part of your lab sandbox — without needing to write configuration files.
Through the UI, you can define exec settings such as the script content, execution mode (local or remote), timeout, environment variables, and output handling. For remote execution, you can either create a new container or target an existing one, with support for network attachments, volume mounts, and user configuration.
Exec resources are ideal for tasks like installing dependencies, configuring services, running build scripts, and initializing databases during lab setup.
For more information on the exec sandbox resource, please refer to the Exec Reference documentation.
Execution modes
Section titled “Execution modes”The exec resource supports three distinct execution modes:
- Local execution — Runs the script directly on the host machine. Supports working directory configuration and daemon mode for background processes.
- Remote execution (new container) — Creates a new container from a specified image and runs the script inside it. Supports network attachments, volume mounts, and user configuration.
- Remote execution (existing container) — Runs the script inside an already running container by selecting it from a list of existing ones. Useful for operations that need to interact with container-specific state.
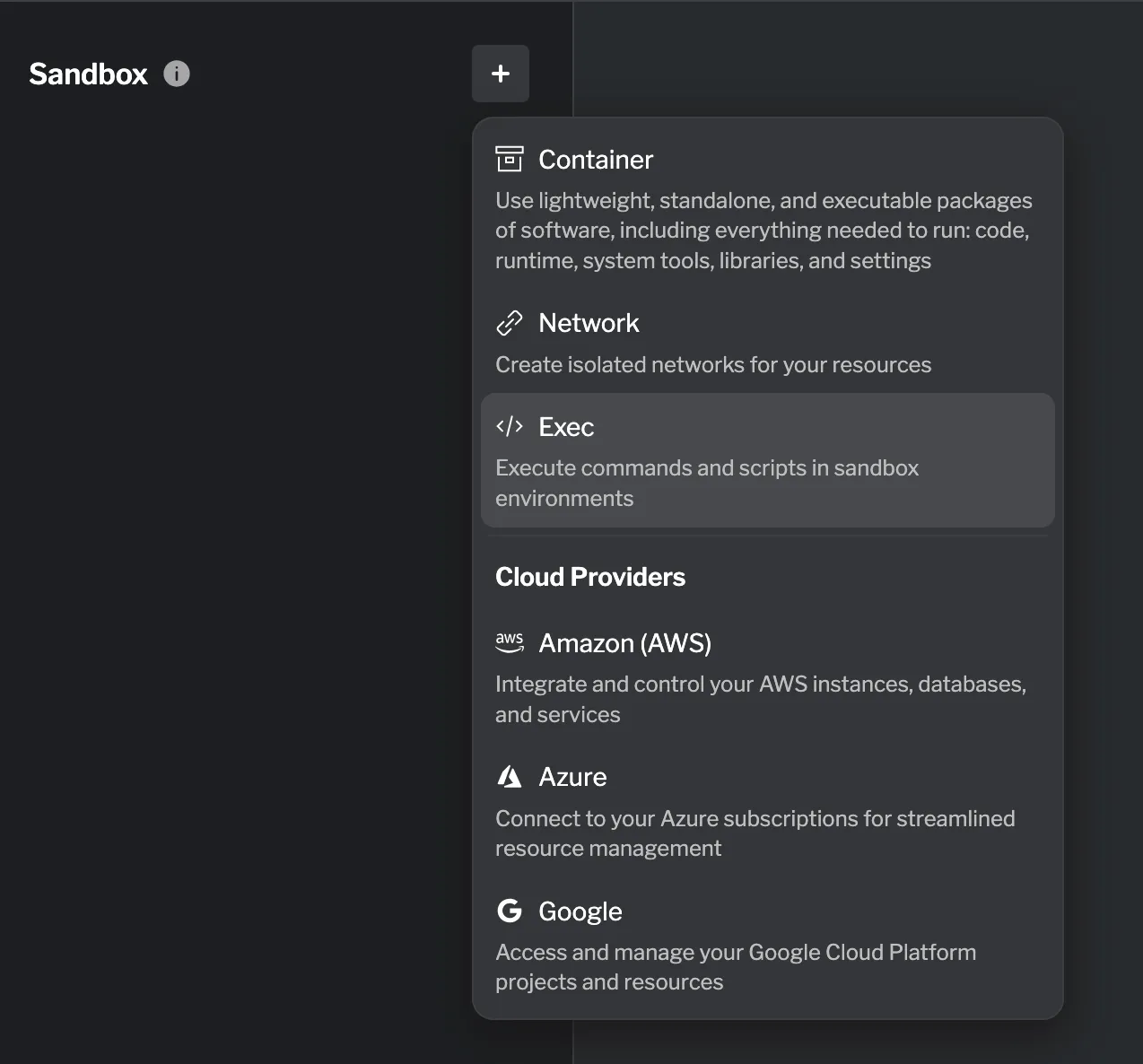
Creating an Exec resource
Section titled “Creating an Exec resource”Exec resources can be created in the Sandbox tab. To create a new Exec resource, navigate to the Sandbox tab and click the + button. Select Exec from the dropdown menu.
Start by naming the exec resource. Note that this is an internal name. You must provide a script to execute, and optionally configure the execution mode, timeout, environment variables, and other settings.
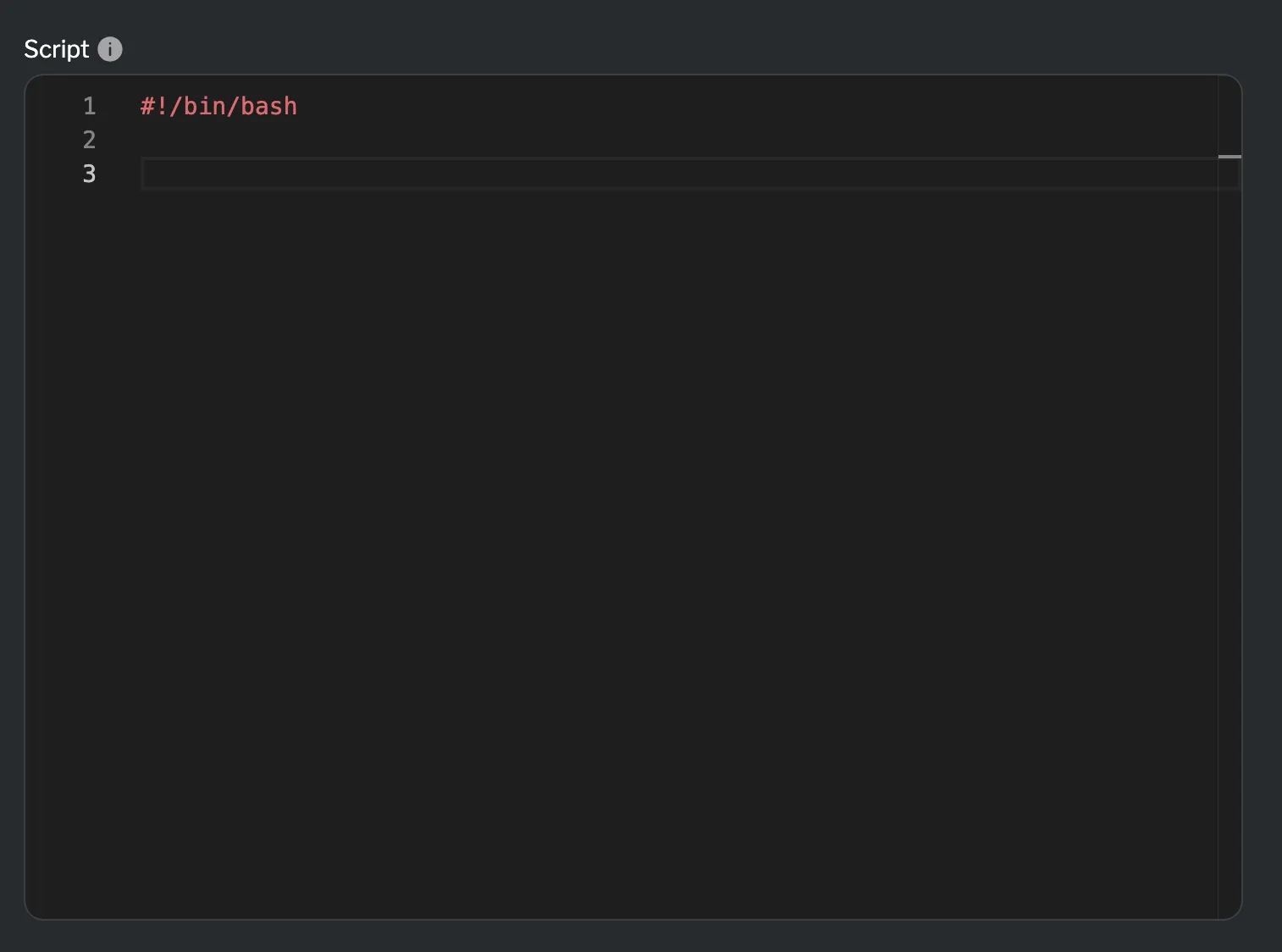
Setting the script
Section titled “Setting the script”The Script field is the core of the exec resource, where you write your script directly in the code editor.
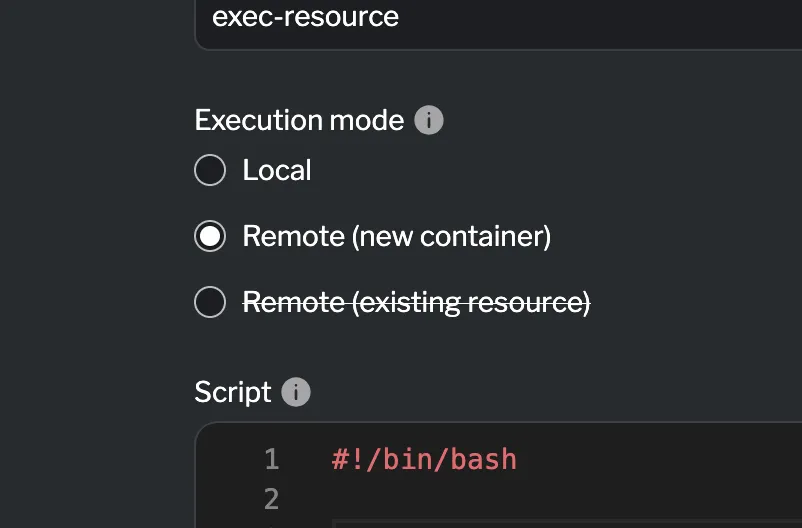
Choosing an execution mode
Section titled “Choosing an execution mode”By default, the exec resource runs in local mode on the host machine. To run the script remotely, you can either:
- Specify an image to create a new container for execution.
- Set a target to run the script inside an existing container.
Editing an Exec resource
Section titled “Editing an Exec resource”To edit an exec resource, select it from the list of existing sandboxes in the Sandbox tab. Click on the exec resource you want to edit, make your changes in the configuration panel, and then click Add changes to save your updates.
Configuration
Section titled “Configuration”General
Section titled “General”| Field | Required? | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Script | ✓ | Script content to execute | |
| Timeout | 300s | Maximum execution time (Go duration string) | |
| Environment | Key-value pairs for environment variables |
Local execution
Section titled “Local execution”These fields are only available when running in local mode (no image or target specified).
| Field | Required? | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Working Directory | Working directory for script execution | ||
| Daemon | false | Run the script as a background daemon process |
Remote execution (new container)
Section titled “Remote execution (new container)”These fields are available when specifying an image to create a new container.
| Field | Required? | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | ✓ | Docker image name with tag |
Network
Section titled “Network”| Field | Required? | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network ID | ✓ | Reference to a network resource | |
| IP Address | Static IP address (auto-assigned if not set) | ||
| Aliases | Network aliases for the container |
Volume
Section titled “Volume”| Field | Required? | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Source | ✓ | Source path or volume name | |
| Destination | ✓ | Mount path inside the container | |
| Read Only | false | Mount the volume as read-only |
Run as
Section titled “Run as”| Field | Required? | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| User | ✓ | Username or UID | |
| Group | ✓ | Group name or GID |
Remote execution (existing container)
Section titled “Remote execution (existing container)”| Field | Required? | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target | ✓ | Reference to an existing container resource |
Summary
Section titled “Summary”The Exec resource provides flexible script execution capabilities for automating setup tasks, system configuration, and custom workflows in your lab sandbox. You can run scripts locally on the host or remotely inside containers — either by creating a new container from an image or by targeting an existing one.
With support for environment variables, output capture, timeouts, and advanced container options like volumes, networks, and user configuration, exec resources give you fine-grained control over your lab’s automation without needing to write configuration files.
